Researchers Develop Model to Help Cities Meet Needs of EV Users Without Overloading Power Grid
Posted: May 22, 2025
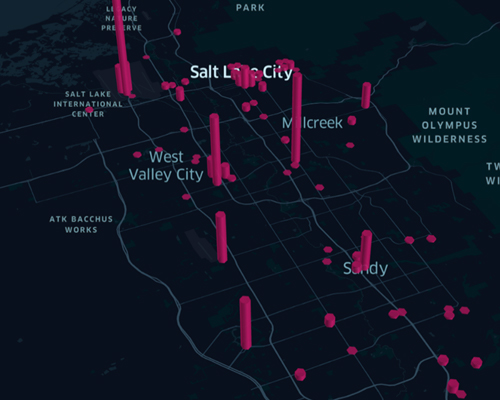 With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in rapidly growing regions like metropolitan areas, efficient deployment of charging infrastructure is critical to avoid overloading the power grid and to meet the charging needs of EV users. Researchers at the University of Utah developed a framework capable of modeling the spatiotemporal distribution of public charging demand and provide practical support for future public charger installations. By using real-world charging data to validate the simulation results, the optimized network was able to reduce the number of EV drivers with zero state-of-charge by 20% and decrease the average charging time from 2.8 hours to 2.5 hours. Additionally, the model identified areas in a metropolitan region with high charging demand but insufficient charging infrastructure, highlighting the need for strategic planning in expanding charging networks. The research has important implications for cities seeking to accelerate EV adoption while ensuring that public charging infrastructure can meet future demand. The outcomes provide actionable insights for urban planners and policymakers, offering a scalable framework for optimizing public EV supply equipment deployment to support sustainable transportation systems.
With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in rapidly growing regions like metropolitan areas, efficient deployment of charging infrastructure is critical to avoid overloading the power grid and to meet the charging needs of EV users. Researchers at the University of Utah developed a framework capable of modeling the spatiotemporal distribution of public charging demand and provide practical support for future public charger installations. By using real-world charging data to validate the simulation results, the optimized network was able to reduce the number of EV drivers with zero state-of-charge by 20% and decrease the average charging time from 2.8 hours to 2.5 hours. Additionally, the model identified areas in a metropolitan region with high charging demand but insufficient charging infrastructure, highlighting the need for strategic planning in expanding charging networks. The research has important implications for cities seeking to accelerate EV adoption while ensuring that public charging infrastructure can meet future demand. The outcomes provide actionable insights for urban planners and policymakers, offering a scalable framework for optimizing public EV supply equipment deployment to support sustainable transportation systems.
Xiaoyue "Cathy" Liu, Ph.D.
University of Utah
A Microscopic Approach for Electric Vehicle Demand Estimation
MPC-24-566